
| RTOS | |
| TCP/IP | |
| •CMX-FFS | |
| •CMX-FFS-TINY | |
| •CMX-FFS-FAT | |
| •CMX-FFS-SAFE-FAT | |
| •CMX-FFS-THIN | |
| USB | |
| CANOpen | |
| Compilers | |
| Modeler | |
CMX-FFS-THIN
|
CMX-FFS-THIN is a full-featured, PC compatible file system for embedded device developers with limited resources available, and wish to add devices to their products that require a FAT12/16/32 media support. The code has been highly optimized for both speed and footprint to allow the developers to extract the most out of their system with a minimum of effort. Typical usage includes adding a Compact Flash card or a Multimedia card to a device. The system includes pre-tested sample drivers for ease of development. The API is standard and easy to use - sample applications in source code are provided to ensure quick integration. Hardware reference designs are also available. Key Features 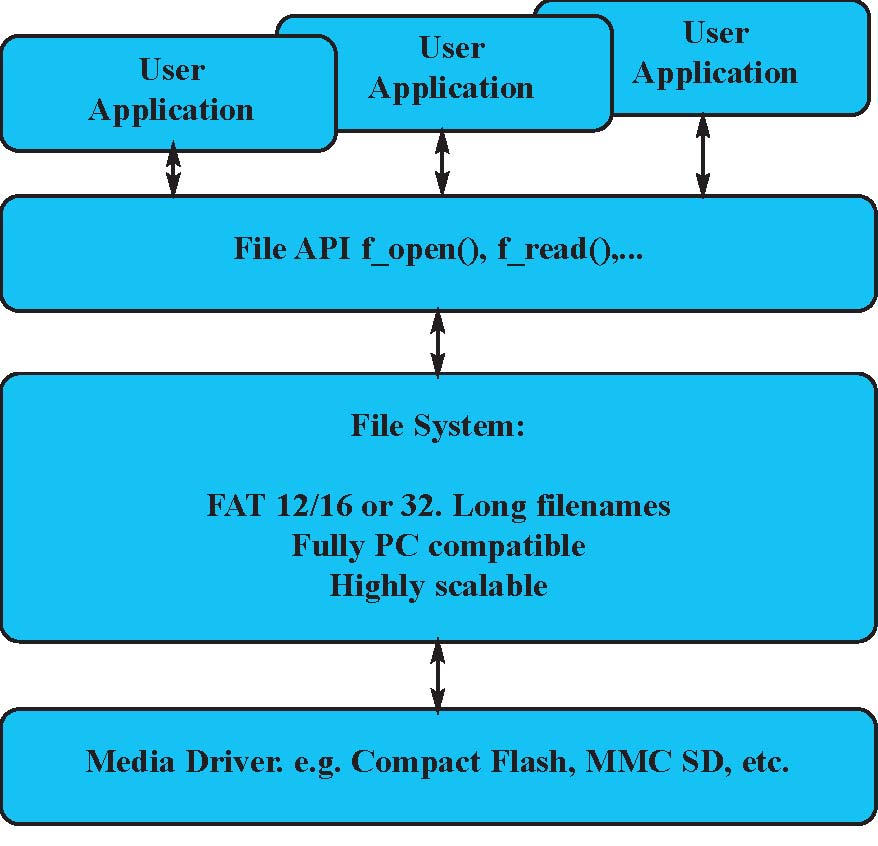
CMX-FFS-THIN is a derivative of the widely used CMX-FFS-FAT system. CMX-FFS-THIN has been compiled and verified with many development environments to guarantee the highest possible level of portability. The User implementation guide contains detailed information for porting the system. CMX-FFS-THIN is virtually agnostic in regards to operating systems and is provided with a RAM drive which enables a system to be run independently of any hardware constraints, such as the availability of a new hardware hardware interface. Typically, customers have a file system up and running within hours of receiving the system! An optional Flash Translation Layer is offered providing a reliable interface for NAND flash DataFlash. This Translation Layer allows the file system to manage flash and provides a logical sector interface to the embedded host. The Flash Translation Layer can support up to 4 Terabytes for each array, provides 528, 2112 and 4224 byte pages and supports all standard NAND devices. CMX-FFS-THIN includes a wealth of build options to enable developers to build exactly the system they need and no more. Hardware Design and Implementation CMX Systems, Inc. has a variety of hardware reference designs available for different hardware platforms and for different peripheral types. These designs include 8-bit to 32-bit platforms. For a particular environment please contact CMX directly. Application Programmer's Interface A full suite of API functions is provided. The routines are entirely standard except that their names have been changed to avoid library conflicts, i.e., fopen() has become f_open(). These routines allow easy initialization and management of multiple volumes, directories and long filenames with complete wild card support. The complete list of API functions is provided below.
Driver Interface The interface between the file system and the physical devices attached is through the driver interface. This interface is simple and straightforward to implement and is complemented by a set of sample drivers and detailed documentation. The functions that must be implemented in any driver are listed below:
Also provided is a set of tested sample drivers to make porting as straightforward as possible. These include:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Copyright material 2014© All Rights Reserved. Site and all contents are the sole property of CMX Systems, Inc.
No part of this site may be copied or used without the express written permission of the owner.
Web Services by Unicorn Web Development, Inc.